Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takai, Toshihide; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Watanabe, Shigeki*; Ishioka, Noriko*
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 9(4), p.21-00397_1 - 21-00397_11, 2022/08
For the mass production of astatine-211, a promising radiopharmaceutical for cancer treatment, the National Institute for Quantum and Radiological Science and Technology has proposed the innovative "Liquid Bismuth Target System." The target window in this system must be made from a material that resists the highly corrosive liquid bismuth environment. To meet this requirement, a promising target window material was selected in corrosion experiments performed in stagnant liquid bismuth. Based on knowledge of corrosion in liquid lead-bismuth eutectic gained during the development of fast reactors and accelerator-driven subcritical systems, experiments were carried out under saturated dissolved oxygen and low oxygen conditions, and the corrosion behaviors of the specimens were evaluated. The FeCrAl-alloy exhibited the most excellent corrosion resistance, followed by FeCrMo-alloy. Both materials are suitable candidates for the target window.
 Li +
Li +  Pb reaction
Pb reactionNishinaka, Ichiro; Yokoyama, Akihiko*; Washiyama, Koshin*; Maeda, Eita*; Watanabe, Shigeki; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Ishioka, Noriko; Makii, Hiroyuki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Yamada, Norihiro*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 304(3), p.1077 - 1083, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:60.27(Chemistry, Analytical)Production cross sections of astatine isotopes 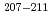 At in the 29-57 MeV
At in the 29-57 MeV  Li induced reaction with
Li induced reaction with  Pb target have been measured by
Pb target have been measured by  - and
- and  -ray spectrometry. Excitation functions of production cross sections have been compared with a statistical model calculation to study the reaction mechanism of
-ray spectrometry. Excitation functions of production cross sections have been compared with a statistical model calculation to study the reaction mechanism of  Li +
Li +  Pb. Considerably small experimental cross sections of
Pb. Considerably small experimental cross sections of  At and
At and  At compared with the calculation were clearly observed at incident energies higher than 44 MeV, indicating that the effects of breakup reaction play a role. A chemical separation of astatine from an irradiated lead target has been studied with a dry-distillation method. A complementary way to produce astatine isotopes has been developed.
At compared with the calculation were clearly observed at incident energies higher than 44 MeV, indicating that the effects of breakup reaction play a role. A chemical separation of astatine from an irradiated lead target has been studied with a dry-distillation method. A complementary way to produce astatine isotopes has been developed.
Togawa, Orihiko
JAERI-M 93-022, 35 Pages, 1993/02
no abstracts in English
 Li ion beams
Li ion beamsNishinaka, Ichiro; Yokoyama, Akihiko*; Washiyama, Koshin*; Amano, Ryohei*; Maeda, Eita*; Taniguchi, Takumi*; Murakami, Kento*; Watanabe, Shigeki; Suzuki, Hiroyuki; Ishioka, Noriko; et al.
no journal, ,
In general, an  -emitter
-emitter  At which is a prospective candidate for utilization in targeted alpha radiotherapy is produced through the
At which is a prospective candidate for utilization in targeted alpha radiotherapy is produced through the  Bi(
Bi( He, 2n)
He, 2n) At reaction. In contrast, our project is focusing on the production in the
At reaction. In contrast, our project is focusing on the production in the  Bi(
Bi( Li, 5n)
Li, 5n) Rn reaction. This enables us to supply
Rn reaction. This enables us to supply  At in a
At in a  Rn/
Rn/ At generator system. The daughter
At generator system. The daughter  At (7.2 h half-life) is extracted from the parent
At (7.2 h half-life) is extracted from the parent  Rn (14h), expanding time-frame for transportation and use of
Rn (14h), expanding time-frame for transportation and use of  At. To use astatine and iodine radioisotopes in our project, the excitation functions of
At. To use astatine and iodine radioisotopes in our project, the excitation functions of  Bi(
Bi( Li, xn)
Li, xn)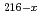 Rn,
Rn,  Pb(
Pb( Li, xn)
Li, xn)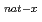 At and
At and  Sn(
Sn( Li, xn)
Li, xn)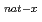 I reactions have been measured. In addition to that, separation techniques have been developed. We report not only on the production and separation of astatine and iodine radioisotopes in the reactions but also on the utilization of those radioisotopes.
I reactions have been measured. In addition to that, separation techniques have been developed. We report not only on the production and separation of astatine and iodine radioisotopes in the reactions but also on the utilization of those radioisotopes.
 Rn/
Rn/ At generator for targeted alpha therapy
At generator for targeted alpha therapyWashiyama, Koshin*; Maeda, Eita*; Yokoyama, Akihiko*; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Taniguchi, Takumi*; Yamada, Norihiro*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Amano, Ryohei*
no journal, ,
A  Rn/
Rn/ At generator for targeted alpha therapy has been developed.
At generator for targeted alpha therapy has been developed.
 At for alpha radiotherapy via
At for alpha radiotherapy via  Bi(
Bi( Li,5n)
Li,5n) Rn
RnNishinaka, Ichiro; Washiyama, Koshin*; Yokoyama, Akihiko*; Maeda, Eita*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Makii, Hiroyuki
no journal, ,
A  Rn/
Rn/ At generator has been proposed to supply a radiotracer
At generator has been proposed to supply a radiotracer  At with a half-life (T
At with a half-life (T = 7.2 h) for medical applications. To establish a technology of the
= 7.2 h) for medical applications. To establish a technology of the  Rn/
Rn/ At generator,
At generator,  Rn (T
Rn (T = 14.7 h) has to be produced through the
= 14.7 h) has to be produced through the  Bi(
Bi( Li, 5n)
Li, 5n) Rn reaction without melting bismuth metal targets due to heat produced by the irradiation of 60 MeV
Rn reaction without melting bismuth metal targets due to heat produced by the irradiation of 60 MeV  Li ion beams. In this work, we have studied the effects of a He gas cooling system of an irradiation chamber constructed for the production of
Li ion beams. In this work, we have studied the effects of a He gas cooling system of an irradiation chamber constructed for the production of  Rn. Irradiations were carried out at the JAEA tandem accelerator using the irradiation chamber equipped with the He gas cooling system. The results show that the He gas effectively cools the targets and the cooling efficiency is nearly independent of the pressure (
Rn. Irradiations were carried out at the JAEA tandem accelerator using the irradiation chamber equipped with the He gas cooling system. The results show that the He gas effectively cools the targets and the cooling efficiency is nearly independent of the pressure ( 1 kPa) and the flow rate (
1 kPa) and the flow rate ( 20 L/min) of the He gas.
20 L/min) of the He gas.
Washiyama, Koshin*; Amano, Ryohei*; Maeda, Eita*; Yokoyama, Akihiko*; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Takahashi, Naruto*; Shinohara, Atsushi*; Watanabe, Shigeki; Ishioka, Noriko
no journal, ,
In order to use of an alpha emitter for targeted alpha therapy, we have started the production and the utilization of  At using 30 MeV
At using 30 MeV  He particle in the
He particle in the  Bi(
Bi( He, 2n)
He, 2n) At nuclear reaction at cyclotron facilities of Osaka University and JAEA Takasaki. In addition to that, we have been developing a
At nuclear reaction at cyclotron facilities of Osaka University and JAEA Takasaki. In addition to that, we have been developing a  Rn/
Rn/ At generator to expand the availability of
At generator to expand the availability of  At to wide range of populations far away from cyclotron facilities. The results of studies on the At-chemistry for clinical use and on the development of the
At to wide range of populations far away from cyclotron facilities. The results of studies on the At-chemistry for clinical use and on the development of the  Rn/
Rn/ At generator will be presented. And a review of current status of targeted alpha therapy in Japan will be also introduced.
At generator will be presented. And a review of current status of targeted alpha therapy in Japan will be also introduced.
 Rn/
Rn/ At generator at the JAEA tandem accelerator
At generator at the JAEA tandem acceleratorNishinaka, Ichiro
no journal, ,
Research and development of a  Rn/
Rn/ At generator has been conducted at the JAEA tandem accelerator. The outline and the current state of the research and development program are presented.
At generator has been conducted at the JAEA tandem accelerator. The outline and the current state of the research and development program are presented.
Toyoshima, Atsushi; Kanda, Akimitsu*; Ikeda, Takumi*; Yoshimura, Takashi*; Shinohara, Atsushi*; Yano, Shinya*; Komori, Yukiko*; Haba, Hiromitsu*
no journal, ,
Astatine (At) is reported to be bound in a few oxidation states in aqueous solutions. However, their valencies and chemical species are experimentally not identified. In this study, we studied redox behavior of At using redox agents and using a flow electrolytic column.  At was produced in the
At was produced in the  Bi(
Bi( , 2
, 2 )
) At reaction and was then separated from the target by a distillation method. Then, redox of At was carried out in 1.0 M HClO
At reaction and was then separated from the target by a distillation method. Then, redox of At was carried out in 1.0 M HClO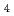 using redox agents or by an electrolysis. After the redox, solvent extraction with HDEHP was performed to identify the redox reactions. Using the redox agents, extraction yields of At were different between the conditions with oxidizing or reducing agents and without redox agents. This means that redox reactions of At can be identified under the present extraction conditions. On the other hand, by the electrolysis, extraction yields of At were almost constant against the variation of applied potential. This is possibly due to the restoration to the original oxidation state after the electrolysis. In the future, we will perform flow electrolytic column chromatography available for simultaneous electrolysis and separation.
using redox agents or by an electrolysis. After the redox, solvent extraction with HDEHP was performed to identify the redox reactions. Using the redox agents, extraction yields of At were different between the conditions with oxidizing or reducing agents and without redox agents. This means that redox reactions of At can be identified under the present extraction conditions. On the other hand, by the electrolysis, extraction yields of At were almost constant against the variation of applied potential. This is possibly due to the restoration to the original oxidation state after the electrolysis. In the future, we will perform flow electrolytic column chromatography available for simultaneous electrolysis and separation.
Toyoshima, Atsushi; Aoyagi, Noboru
no journal, ,
Although carrier-free radiotracers are utilized in lots of research fields, their chemical forms have not been identified by UV/vis. spectroscopy because of their micro quantities. In this study, we are developing an apparatus for cavity ring-down spectroscopy to perform absorption spectroscopy of radioiodine and astatine in a gas-phase. With this apparatus, ultra-sensitive absorption measurement is realized by making injected pulse-laser go back and forth tens of thousand times between facing mirrors. Intensity of laser in the cavity becomes weaker by its escaping through the mirrors and by absorption by samples. Absorption coefficients are obtained from difference in the life-time of escaped light between blank and sample measurements. Chemical species are expected to be characterized by measuring absorption coefficients at various wavelength and comparing these with known spectra and theoretical calculations. In the symposium, present status of the development will be reported.
Takai, Toshihide; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Watanabe, Shigeki*; Ishioka, Noriko*
no journal, ,
For the mass production of astatine-211, a promising radiopharmaceutical for cancer treatment, the National Institute for Quantum and Radiological Science and Technology has proposed the innovative "Liquid Bismuth Target System." The target window in this system must be made from a material that resists the highly corrosive liquid bismuth environment. To meet this requirement, a promising target window material was selected in corrosion experiments performed in stagnant liquid bismuth. Based on knowledge of corrosion in liquid lead-bismuth eutectic gained during the development of fast reactors and accelerator-driven subcritical systems, experiments were carried out under saturated dissolved oxygen and low oxygen conditions, and the corrosion behaviors of the specimens were evaluated. The FeCrAl-alloy exhibited the most excellent corrosion resistance, followed by FeCrMo-alloy. Both materials are suitable candidates for the target window.